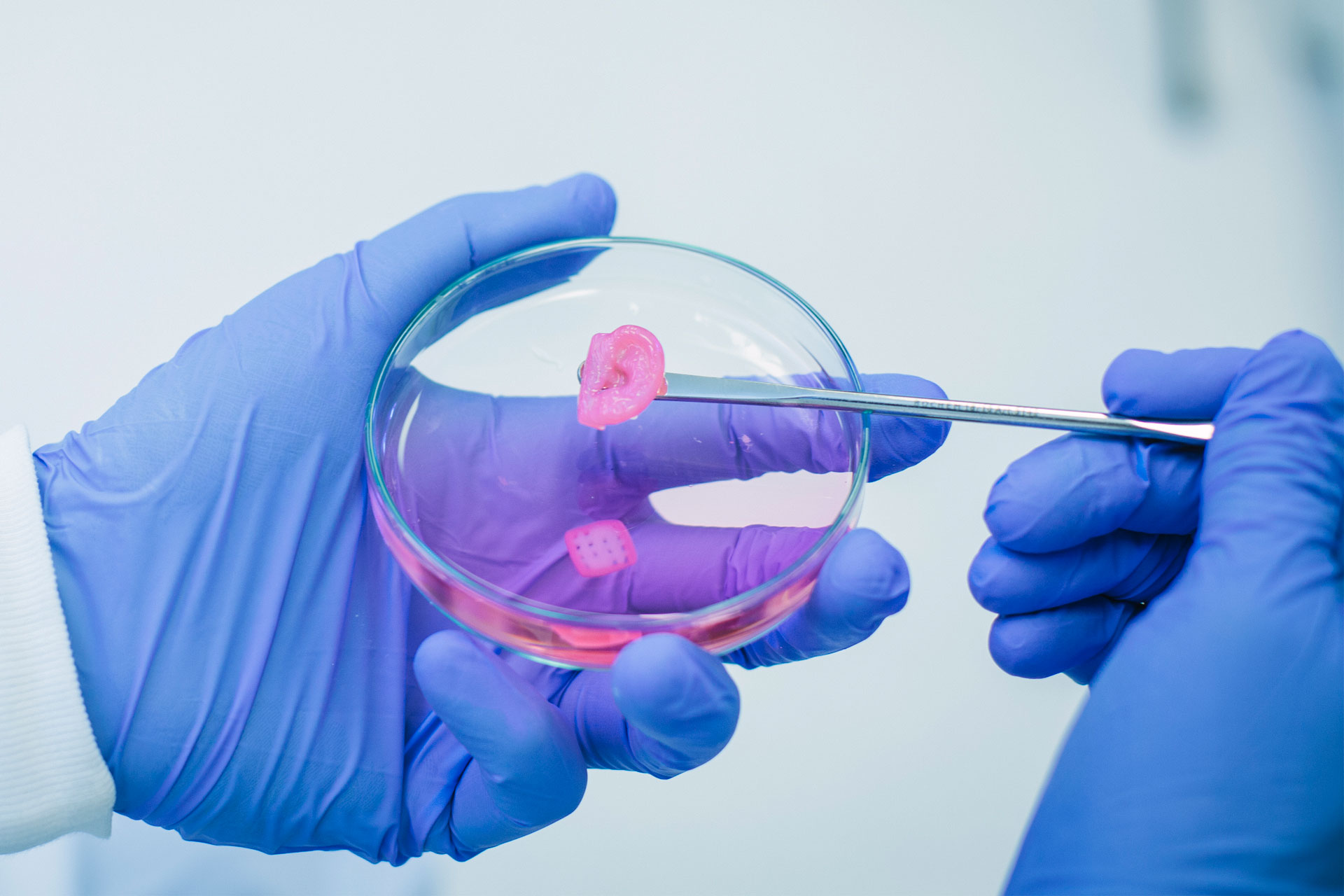
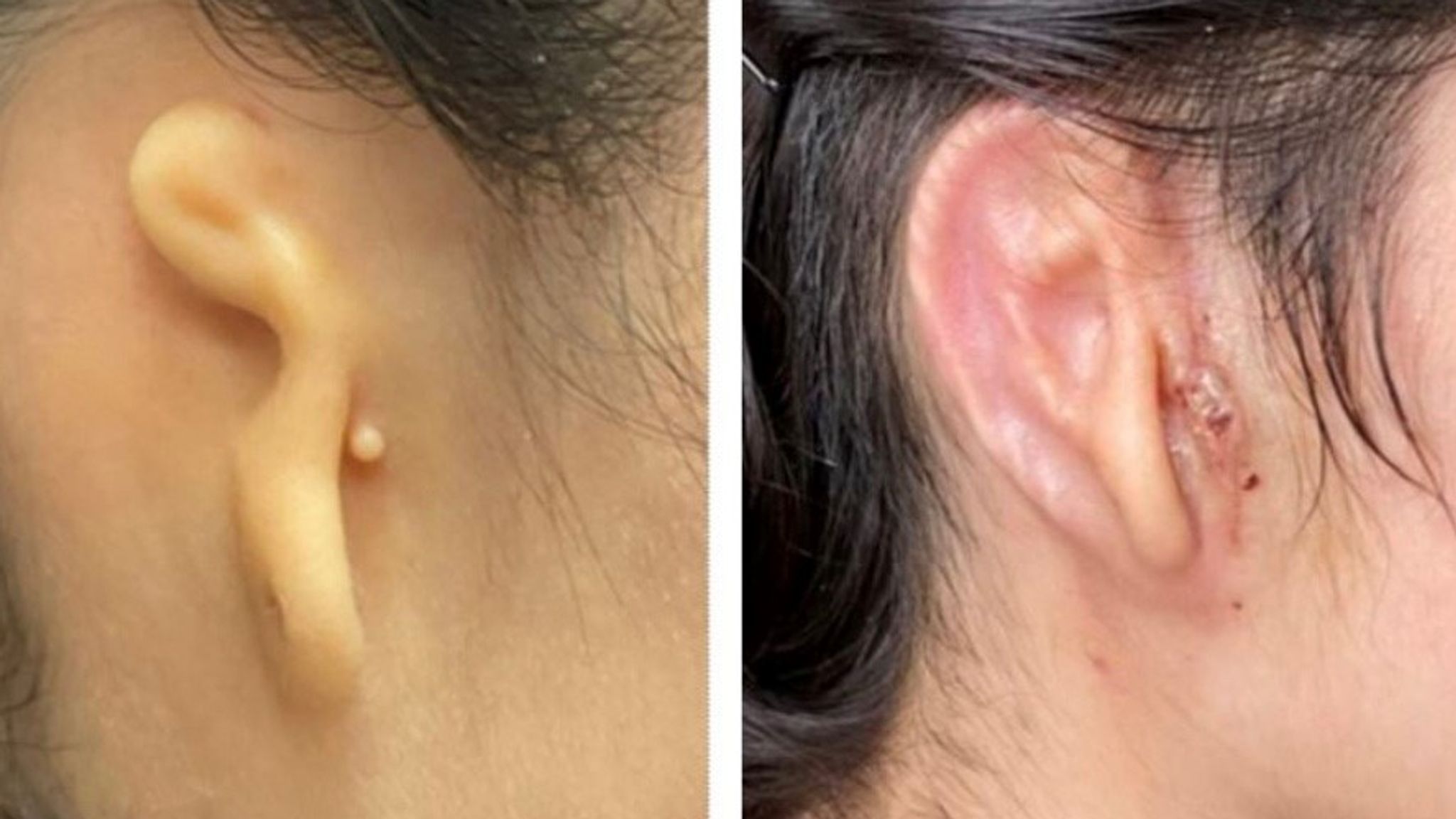
Bioprinting technology involves bioink and biomaterials that are mixed with cells, used as the printing material for 3D printing. This involves techniques like cell culturing, growth factors, and using the bioink and biomaterials to fabricate biomedical parts to imitate tissue characteristics (involving tissue engineering) and form functional biofilms. Unlike normal 3D printers, bioprinters utilise bioinks are designed to print biological materials specifically.
Inkjet 3D bioprinting is a type of bioprinting technology. Some benefits of this technology is its high speed and availability.
The first 3D printed organ, bladder, was transplanted into a human in 1999.