Can lab-grown meat be a more ethical food solution?
Recently, a number of my family became meat free. As a lover of chicken nuggets, I was surprised by this, with the scientist in me concerned about the potential drop of protein ingestion. Naturally I was curious about this change, and subsequently gained understanding of how detrimental conventional meat farming is to the environment, the harm to the animals and the cost involved. I recently attended a lecture about tissue engineering and was made aware about how it could be used to grow meat in a laboratory and did more research to determine whether this would be an improved method of meat farming and I believe it is.
Greenhouse gas emissions from livestock represent 14.5% of emissions
A Global Assessment of Emissions and Mitigation Opportunities, Food And Agriculture Organization of The United Nations (FAO), Rome 2013.
The Science of Tissue Engineering
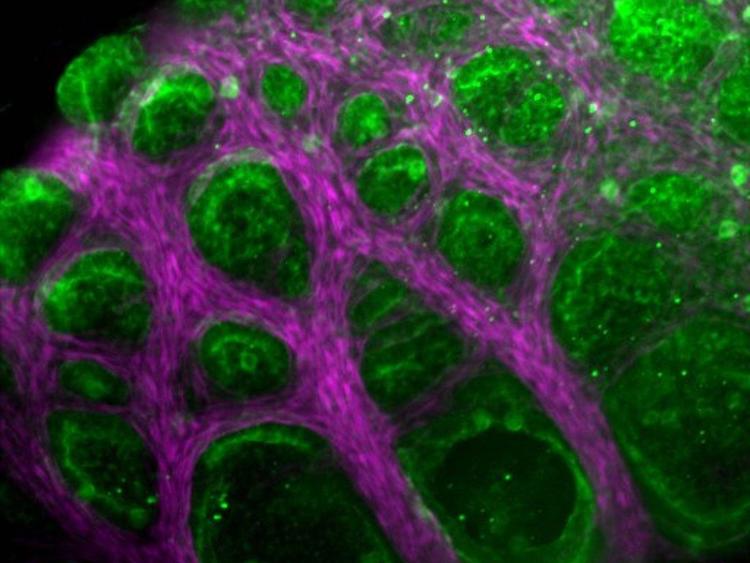
Tissues are made up of cells and an extracellular matrix ; this is anything in a tissue not located inside a cell and is produced by the cells themselves. Tissue engineering involves combining the living component of tissues (cells) with a scaffolding material for structure and then placing it in a growth media for development. There are a range of scaffolding materials available some are biodegradable and some are not.
Cooking 101 : How to grow your own meat
Meat sold in stores is mostly muscle tissue from the animal it’s harvested from with some fat tissue so could be grown in a tissue engineering lab.
- The process begins by extracting cells from an animal, a small sample is taken from an animal under anaesthesia by a trained professional.
- Myosatellite cells (multipoint muscle stem cells) can be extracted and placed in bioreactors with a growth medium that mimics the natural environment the cells would experience as part of an animal (access to oxygen, nutrients and minerals need for differentiation/growth).
- Changes in the media composition ,usually cued by addition or activation of the scaffolding material, initiates the differentiation of the muscle stem cells allowing formation of skeletal muscle cells, fat cells and connective tissue.
- The differentiated cells are harvested, prepared and packaged before being sent off to be sold in stores.
Certain variables like the size of the meat being produced, the growth medium used, the number of stem cells you start with determines the time it takes for this process to occur. Current methods place the timeline between 2-8 weeks which is much faster than rearing an animal from birth for their meat.
Benefits, Limitations and Ethics
Watch this short video to see the benefits of the production process of lab cultivated meat environmentally, to animal welfare and eventually financially.
The main limitations of lab grown meat include:
- Scaffolding materials are unable to supply oxygen and nutrients to larger tissues like muscle
- Developing these technologies will be expensive so first generation products might not be affordable to the average household
The main ethical implications are:
- Animals must still undergo a procedure to extract the cells
- If the scaffolding material cannot be removed from the end product a hybrid product will be formed as there are no animal based scaffolds currently available.
My Opinion
However, I believe that like me, when people become more aware about the negative effects that large cattle farms have on the environment, how much more cost effective meat production could be as technology advances and ,the biggest reason, that no more animals have to die or be raised solely to be eaten, lab grown meat will rise in popularity and will be properly invested in as an industry.

