In the intricate landscape of medical science, perhaps no feat is as remarkable as the creation of artificial hearts. These remarkable devices stand as a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of innovation in healthcare. As we stand at the cusp of a new era in medicine, it’s important to explore the history, current challenges, and the promising future of artificial hearts.
A Journey Through Time: The History of Artificial Hearts
The genesis of artificial hearts can be traced back to the 1950s when Dr. Paul M. Zoll developed the first external pacemaker. This monumental achievement laid the foundation for further advancements in cardiac care. However, it wasn’t until 1982 that Dr. Robert Jarvik’s creation, the Jarvik-7, became the first artificial heart implanted in a human. Though it was initially intended as a temporary measure, it marked a significant milestone in medical history.
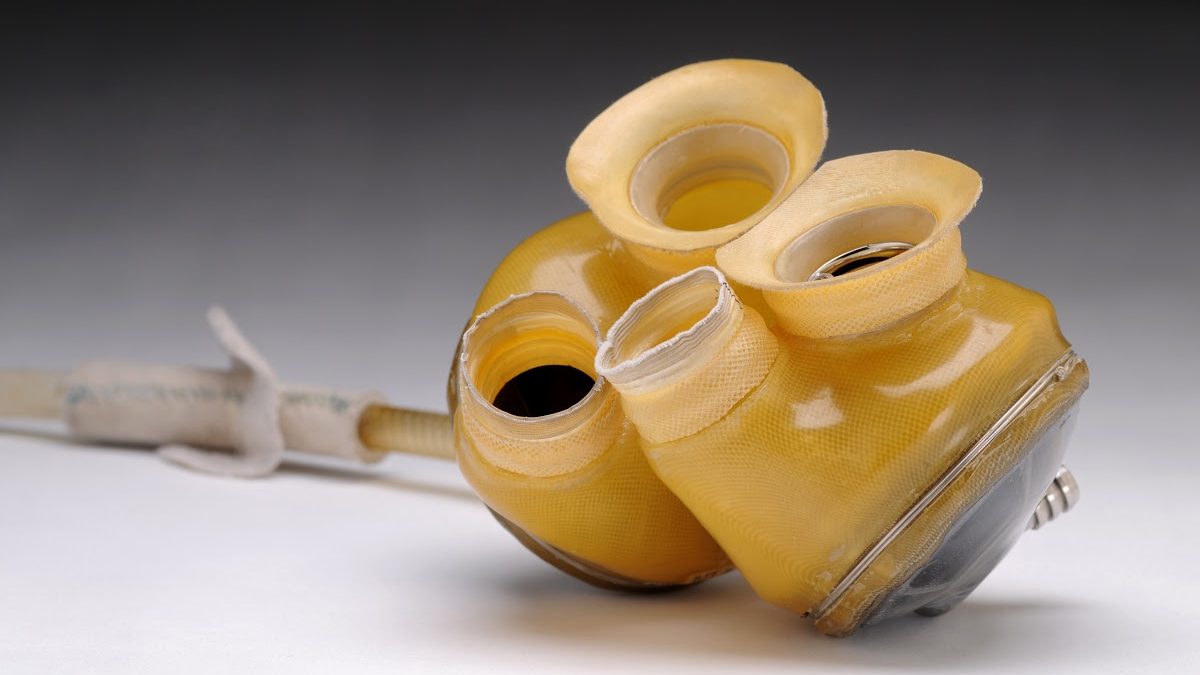

The Present Landscape: Temporary Solutions Amidst Growing Challenges
Today, artificial hearts primarily serve as a bridge for patients awaiting heart transplants. However, the demand for heart transplants far exceeds the available supply. One of the most significant challenges facing artificial hearts is the interaction between platelets and artificial surfaces, which triggers the activation of contact proteins and leads to coagulation. Consequently, patients require therapeutic intervention, often in the form of medications, to mitigate these effects. However, despite these efforts, there are inherent limitations on the duration for which artificial hearts can be utilized due to this phenomenon.
In the UK, the British Heart Foundation reports that over 900,000 people live with heart failure, with an estimated 1,000 new cases diagnosed each month. Each year, around 200 people in the UK are added to the heart transplant waiting list. Regrettably, due to the scarcity of donor organs, many patients face the grim reality of heart disease, facing long stays in hospital with some tragically passing away while awaiting a life-saving transplant.
Looking Forward: The Promise of Future Artificial Hearts
As we venture into the future of artificial hearts, a myriad of technological advancements offer hope for overcoming current limitations and revolutionizing cardiac care. One area of significant progress lies in battery technology. Traditional power sources for artificial hearts, such as external batteries or power cords, present challenges in terms of mobility and infection risk. However, the development of smaller, more efficient batteries promises greater freedom and convenience for patients, allowing them to lead more active lives without constant tethering to external power sources.
Biomaterials also play a pivotal role in the advancement of artificial hearts. Researchers are exploring innovative materials that closely mimic the properties of natural heart tissue, reducing the risk of immune rejection and clot formation. These biocompatible materials not only enhance the longevity of artificial hearts but also promote better integration with the surrounding tissues, minimizing the need for anticoagulant therapy and reducing the risk of complications.
Incorporating advanced sensors into artificial hearts enables real-time monitoring of vital parameters such as blood flow, pressure, and heart rate. This continuous stream of data allows for early detection of potential issues, enabling timely intervention and improving patient outcomes.