Neuralink
Human testing experiments have been a controversial topic in the science field. A recent news article came across me. Neuralink, a ‘medical research’ company founded by Elon Musk in July 2016, reported that the first chip brain, ‘Telepathy’, was being implanted into the human brain.

‘Telepathy’ was designed for the disabled who have lost the use of their limbs. The human clinical trial was first opened for patients with restricted or zero available use of upper arms caused by cervical spinal cord injury or by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a fatal motor neuron disease about degeneration of nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain. By placing a tiny, wireless brain chip on the surface of the brain attached to the cortex, movements could be revived by the intention to move.
Neurological mechanism of neurons
The brain consists of nerve cells called neurons, which transmit signals and messages over the body afferently and efferently.
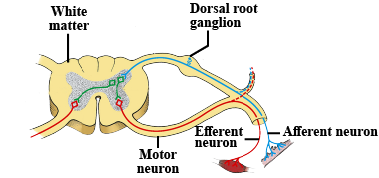
Afferent neurons refer to receiving stimulations and sending signals from the environment through the spinal cord to the brain. Efferent neurons do the reversing way, sending motor signals from the brain to the peripheral nervous system in order to initiate movements.
The electrodes in the Neuralink chip are responsible for reading these afferent signals, translating them into efferent signals and turning them into motor movements.
Human experimentation
The largest controversy of human experimentation is said to be unethical. Pseudoscientific frameworks like race science are argued to be not ethical. This also raises problems with informed consent, in which research subjects freely volunteer to participate after being made aware of the potential dangers and benefits. However, past incidents where participants were misinformed about the real purpose of the experiment, such as the Tuskegee Syphilis Study in the United States, have brought attention to the significance of informed consent. It also includes torturing people which causes them to be mentally or physically injured. During the experiment, the research subject may be exposed to risks from physical injuries to psychological distress. To balance the benefits of the study and the potential risk to the subjects is the biggest concern a scientist should be aware of.
In May 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration gave the approval for Neuralink’s human clinical trials. However, the specific approach of how Neuralink balances between experimenting and the risk of reseach subjects might face is still unknown.
Conclusion
Similar to other implants in the human body, Neuralink brain implants may result in unfavourable consequences like inflammation and scarring. Additional problems might be bleeding or hardware-related concerns with the implant. Of course, it is still a very new technology and still requires a lot of research and experiment, but it’s a hope for patients with spinal cord injury to move again. Overall, with suitable and appropriate observation under medical and neurological professionals, the brain implant could be a direction for patients to live more conveniently than before.