Introduction
This object seeks to convince the student of the distortions present in raw imagery and the need for orthorectification.
Reflection
If we look at the following aerial photos, we notice that some of the features do not appear to visually reflect their real world positional alignment. This is due to relief displacement. If we want to use aerial photos for surveying and planning then we have to remove such geometric errors. Before considering how we can remove such errors automatically by computer it is helpful to look carefully at the images.
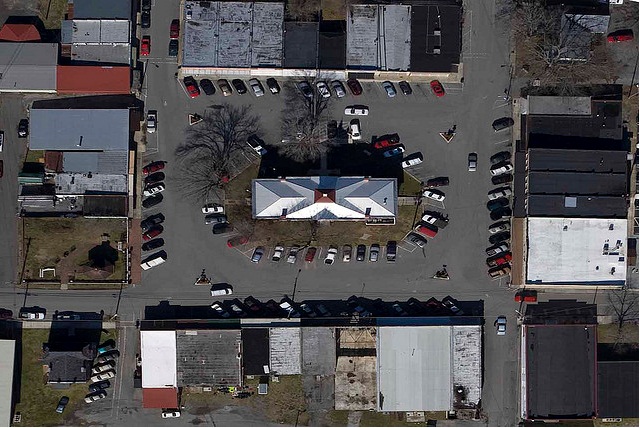


Source: http://www.flickr.com/photos/14917023@N05/2839137664
Activity
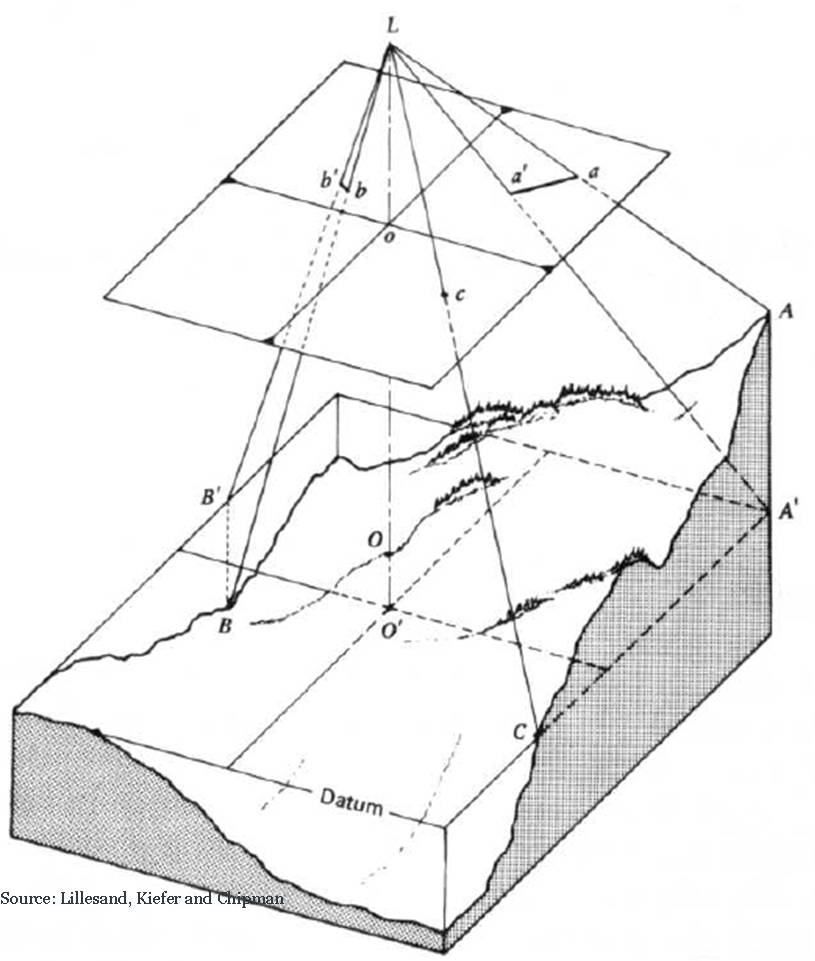
Look at the following diagram. Can you demarcate the positive and negative relief displacement locations?
Positive and Negative Relief Displacement
In the image there are areas which are below the mean height,and other areas above. In such cases the displacements will be in different directions (inward or outward). The point B is below the average height, and point A is above. We know that tall objects are displaced away from the centre of the photo. Though the points A and A' are located at the same point, in the image a is displaced than a'. Similarly the point B and B' are at the same location but B is displaced inward (towards) the center. The Point A has undergone positive relief displacement, and B has undergone negative relief displacement.
Overall, the north east region of the image would have positive relief displacement, and the south west region would have negative relief displacement.
You should by now be convinced that raw aerial photos cannot show features in their correct locations due to relief displacements caused mainly by terrain relief/height of objects (and also due to attitude of the camera). Ground objects resting on different elevations exhibit disparities or displacements in their image position. You should also be aware of the issue of perspective of the imaging system. The amimation below provides a revision of perspective and orthographic image projections.
In vertical (or oblique) photos, displacements of objects are obvious. Representation of the features without positional deformities involves a series of procedures based on mathematical bases to remove the errors. This process is known as orthorectification and is the subject of this unit. The resultant rectified photo is designated as an orthophoto or orthoimage (if the raw image from a satellite sensor). Orthoimages are conceived as planimetrically error-free data. Therefore they are treated as reliable and effective sources of information for municipal planning, cadastral mapping, and GIS applications.
References
The list below contains a general reading list on digital orthophotography, including a range of references available online.
Horn, B. K. P. (1989) Relative orientation [Online]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology: The Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. http://people.csail.mit.edu/bkph/papers/Relative_Orientation.pdf
Linder, W. (2009) Digital Photogrammetry: A Practical Course, The Netherlands, Springer.
Novak, K. (1992) Rectification of digital imagery. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 58, 339-344.
Okeke, F. I. (2009) Review of Digital Image Orthorectification Techniques.
Schowengerdt, R. A. 2007. Remote Sensing: Models and Methods for image processing, California, US, Elsevier.