Modelling Space-Ground Geometry
This learning object introduces different modelling approaches for describing the space-ground geometry and briefly outlines the rational polynomial coefficients (RPC) model.
In aerial photogrammetry, the collinearity condition, stereo model formation, orthorectification and space intersection and related issues are all important concepts required in deriving accurate information about terrain height (Z) and position (X,Y). In order to achieve this we need to build a proper camera-ground model. In the frame-capturing mode (as in an aerial system) it is very easy to build this camera-ground model, but in satellite mode (line by line) it is more complex. There are two groups of models being used to achieve this: the rigorous sensor model and replacement sensor model.
In the rigorous sensor model, the physical imaging system is reconstructed using the collinearity condition. Due to the limitations in accurately obtaining the required dynamic physical parameters, this approach is not fully reliable for satellite data. Hence, the replacement sensor model is needed. This model depends purely on a mathematical basis. There are 3 varieties within this model: the grid interpolation model, rational polynomial coefficients (RPC) model and universal real time sensor model. These models are very complex to describe. Hence only the RPC model is briefly explained here. Students should read the articles indicated in the reading activity to learn about these models in greater depth.
RPC model
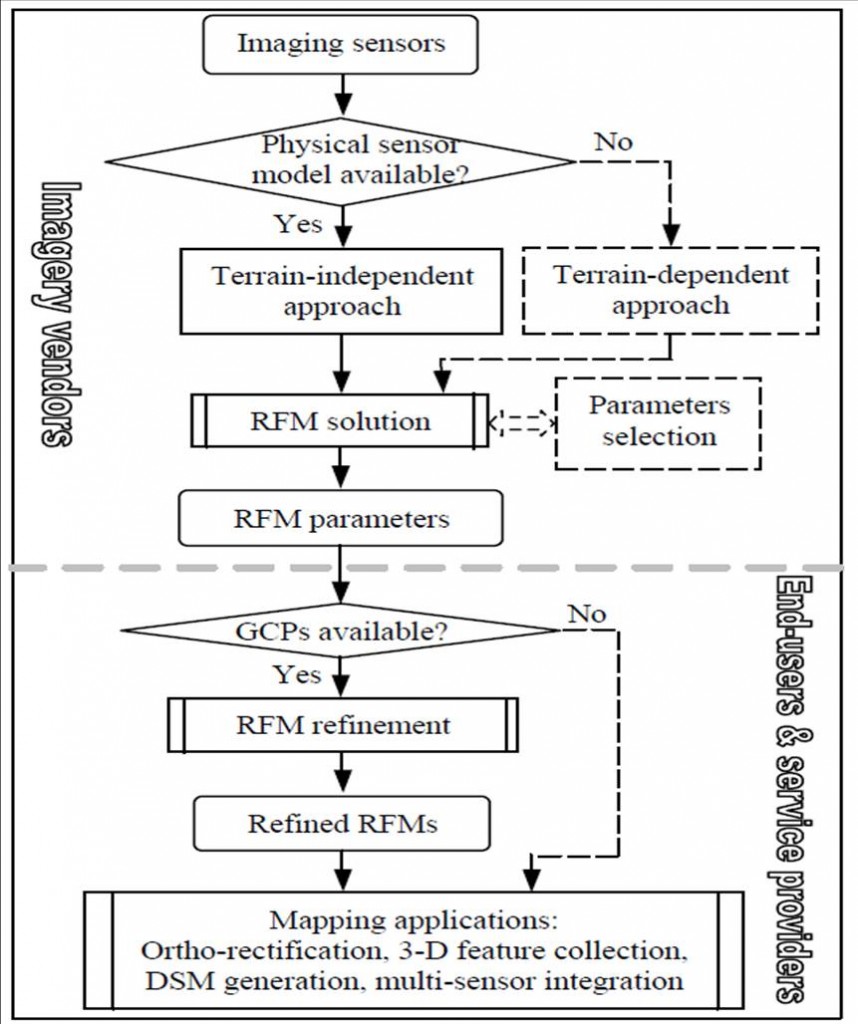
The RPC model uses ratios of cubic polynomials to express the transformation from ground surface coordinates (latitude, longitude, elevation) to image coordinates (line, column) for the particular input image. The user may be required to provide some ground control points to refine and validate the modelled relationship between image and ground. Also with the use of DEM and RPC, automatic orthorectification can be achieved. The model coefficients are mainly provided by the imagery vendors and this information is normally written into the header of the image data.
The following illustration depicts the strategy of the RPC modelling process:
Source: Xu et al. (2004)
Reading Activity
Hu, Y., Tao, V. and Croitoru, A. (2004) Understanding the rational function model: methods and applications Proceedings, ISPRS Congress, Proceedings of Commission IV, Volume XXXV, 423 http://www.isprs.org/proceedings/XXXV/congress/comm4/papers/423.pdf
Bang, K. I., Jeong, S., Kim, K-O. and Cho, W. (2003) Automatic DEM generation using IKONOS stereo imagery. Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS Proceedings. IEEE International 7, 4289-4291
Dolloff, J. (2004) Replacement Sensor Models. 2004 Manual of Photogrammetry (Draft) http://www.gwg.nga.mil/ntb/coordinationitems/RSM%20TRE%20Appendiix%20C_July_23_04.pdf