Recent Comments
Archives
Categories
- No categories
Meta
2.1. Characteristics of a Remote Sensing System
What is Remote Sensing?
Curran 1985 defines it as:
“The use of electromagnetic radiation sensors to record images of the environment, which can be interepreted to yield useful information“.
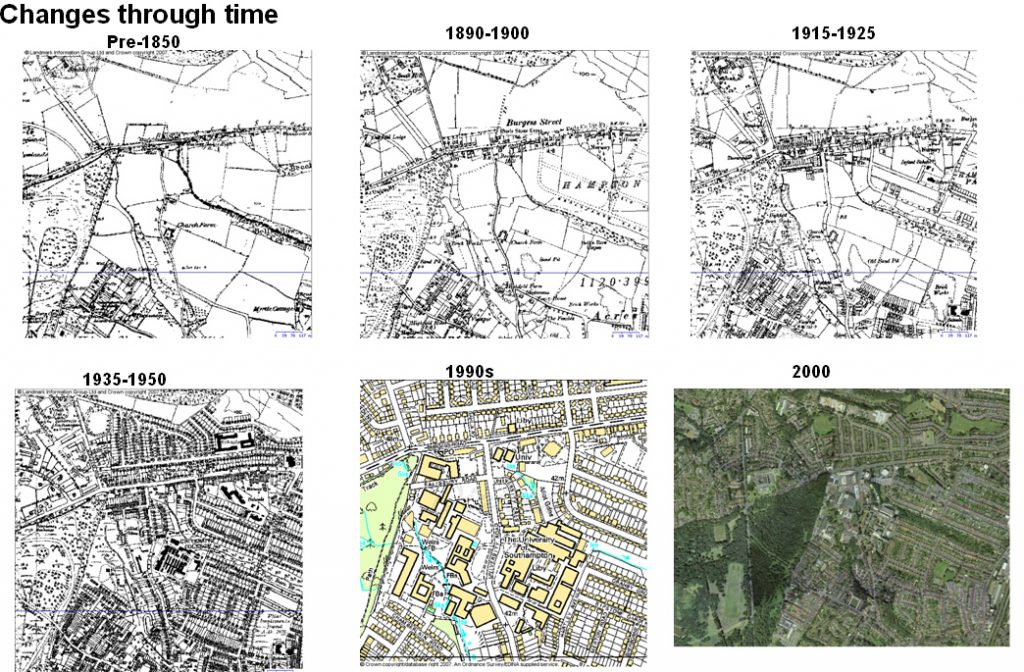
As an example of useful information, consider the changes to the landscape of Southampton University in this graphic:
Reflection
At this moment you are probably looking at a computer screen. What is the analogy between what you and the computer at the moment and a remote sensing system as defined by the three italiacised points in Curran’s definition above?
Show Answer
Activity
Using this tutorial, and Google Earth version 5 or later fly to this location( Lat: 50. 6359, Lon: -1.4133 ) in the Isle of Wight and observe what is happening to the coastline by stepping through the historical remotely sensed images.
Characteristics of Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is characterised by:
- Sensor Stage (satellite, plane, kite, ground based)
- View (angle of view)
- Type of radiation sensed (visible light, infrared, radar)
- Time of capture
It can also be used or re-used for many different purposes. We will look at each of these characteristics in turn
1. Stages
As should be expected, the higher the platform generally the lower resolution the imagery. Satellites vary in altitude but are generally above aircraft, these also vary in altitude with high flying spy aircraft and lower light aircraft. The image below illustrates the difference in resolution that can often be seen in the Google Earth base imagery, generally satellite imagery is being replaced by higher resolution plane based imagery.

Recently a number of very low altitude platforms(UAVs, drones) have started to be used in remote sensing, though there are issues to do with calibration of the images taken by these platforms that still needs to be resolved.
Reflection
What are the two major types of satellite orbit and what are their relative altitudes?
Show Answer
2. Platform View Angle
Sensors can view the earth’s surface at different angles, this reveals different information such as relative heights of objects. This creates confusing representations in Google earth, the image on the left shows one remotely sensed image of a high rise building from an oblique view. On the other side of the road the image has been taken from a similar angle but from the opposite direction.
Note that both images have been processed so that ground positions are correct since oblique images foreshorten the image in the direction of tilt, this is illustrated in the image below.

Reflection
Apart from changing the angle of view, what other characteristic of sensors sampling visible light could be used to reveal object height information?
Show Answer
3. Spectral Bands
Your eyes sample in three colours, red, green and blue, any colour you perceive is a mix of these three primary colours. Remote sensing platforms are not limited to these colours or bands and can sense different wavelengths. For example, they can measure Near Infra Red which shows clearly different colours for vegetation and non-vegetation as can be seen in the images to the left: The right hand image is near infra red and vegetation appears bright red and pink in this image.


Such images can be combined to form ‘false colour images’ where primary colours in display stand in for the original band that was sensed, e.g. red stood in for near infra red in the example image.
4. Time of Capture
The time of capture is useful information to gather as it can be used to track spatial changes. Examine the spread of Las Vegas between 1970 and 2000 in the images below.
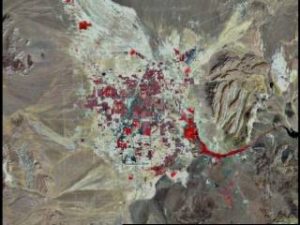
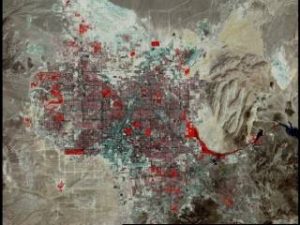
Reflection
Open Google Earth, enter ‘Rondonia Brazil’ in the Search box then click the magnifying glass to fly in. Using this tutorial, and Google Earth version 5 or later use the timeline to see the changes in land use. Use the ruler tool to get a sense of the scale of the changes.
Repeat the exercise for ‘Lake Chad, Nigeria’.
Show Answer
Examples of Use
The following examples use one or a number of types of remote sensing to solve spatial problems:
- Meteorology: Weather forecasting, Climate studies, Global change
- Hydrology: Water balance, Energy balance, Agro hydrology
- Soil science: Soil mapping
- Biology/conservation: Vegetation mapping/monitoring, Forestry Inventories, mapping, de/re-forestation, forest fires
- Enviro studies: Sources/effects of pollution, Agriculture Land use development, water management, erosion
- Planning Physical: Planning scenarios
- Land surveying: Topography, spatial data models, GIS
Reflection
Think of ways the 4 different types of remote sensing could be applied to the problem of forest fires.
Show Answer
References
BBC explanation of vanishing Lake Chad.
