Recent Comments
Archives
Categories
- No categories
Meta
6.3. The SPOT Programme
Objectives
The purpose of this learning object is to introduce the key characteristics of the SPOT Program. Although more recent than Landsat, SPOT is a long-running, multi-satellite system. The learning object briefly describes the history of the program and explains how the characteristics of the sensors used serve to influence the characteristics of the available data.
SPOT (Système Pour l’Observation de la Terre) is a series of imaging satellites designed and launched by CNES, France, with support from Sweden and Belgium. There have been 7 SPOT satellites in total, 2 of which are still operational:

| Satellite | Launch date | Current state |
| SPOT 1 | 22/2/86 | Not in operation(1/11/2000) |
| SPOT 2 | 22/1/90 | Not in operation(30/06/2009) |
| SPOT 3 | 26/9/93 | Not in operation(14/11/1996) |
| SPOT 4 | 24/3/98 | Not in operation(11/01/2013) |
| SPOT 5 | 4/5/02 | Not in operation (31/03/ 2015) |
| SPOT 6 | 9/09/2012 | Still in operation |
| SPOT 7 | 30/06/2014 | Still in operation |
All the SPOT satellites were in near-polar, sun-synchronous orbits at an altitude of 832km above the Earth and cross the equator at 10.30. The revisit periods are 26 days for vertical observations, and approximately 2.5 days if pointed off-nadir: this latter characteristic relates to the unique feature of SPOT that the viewing angle can be changed to look either side of the satellite’s vertical (nadir) track. This off-nadir viewing increases the satellite’s revisit capability. The ability to point the sensors up to 27° from nadir allows SPOT to view within a 950km swath and to revisit any location several times per week.
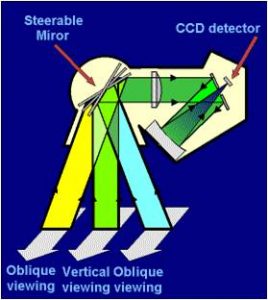
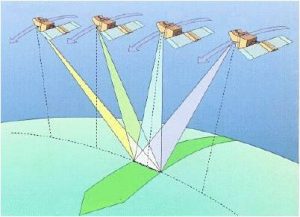
This improves the ability to monitor specific locations and increases the chances of obtaining cloud-free scenes. SPOT’s oblique viewing capacity also makes it possible to produce stereo-pairs, whereby two images of the same area acquired on different dates and at different angles can be combined and used for stereo-plotting, topographic mapping and the production of digital elevation models (DEMs).
N/B: The slides below will not show on the webpage, but you can save/keep them on your computer and view them using the Adobe Flash Player 32 you downloaded earlier
A number of different sensors have been carried on board the SPOT satellites, including:
- High Resolution Visible (HRV) sensor
- High Resolution Visible and Infra-Red (HRVIR) instrument
- High Resolution Geometrical (HRG) sensor
- Vegetation instrument
These have been carried on the different SPOT satellites as follows:
| Satellite | Sensor |
| SPOT 1 | HRV |
| SPOT 2 | HRV |
| SPOT 3 | HRV |
| SPOT 4 | HRVIR/VEGETATION |
| SPOT 5 | HRG/VEGETATION |
| SPOT 6 | NAOMI |
| SPOT 7 | NAOMI |
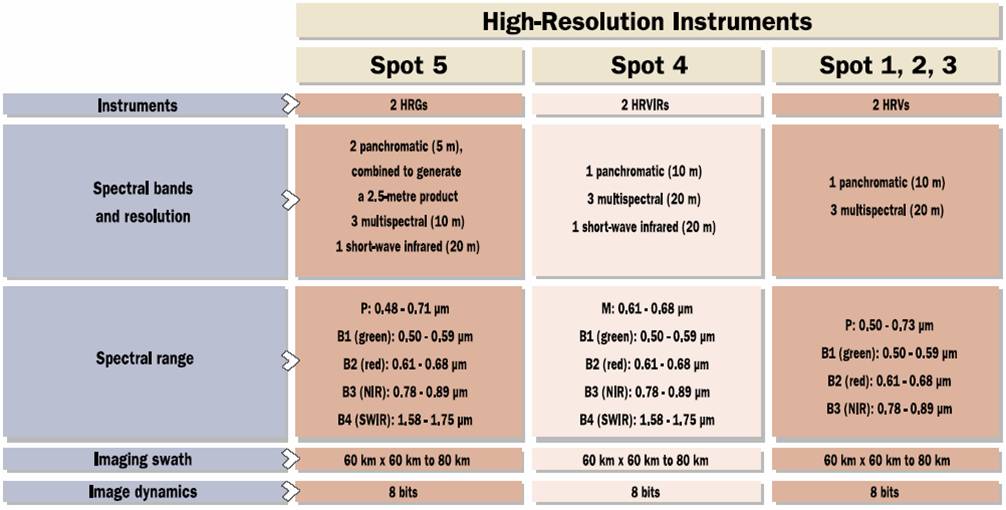
SPOT sensors operated in a twin-viewing configuration (i.e. one in panchromatic mode and one in multispectral mode). Further details of the sensor characteristics are summarised in the figure:
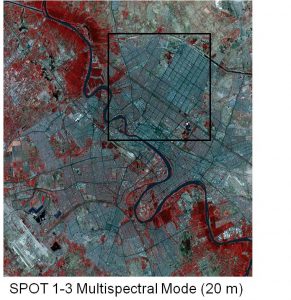
The difference between the SPOT 1-3 MSS 20m and panchromatic 10m modes is illustrated by these images:
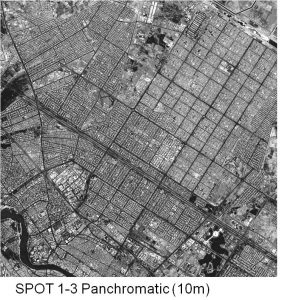
The vegetation instrument carried on board the SPOT 4 and 5 satellites has a wide swath of 2200km at a low spatial resolution of 1km and a high revisit frequency of approximately one day. It thus provides daily monitoring of regional to global scale vegetation cover in the following spectral bands:
| Spectral bands | Wavelength |
| Blue | 0.43-0.47 µm |
| Red | 0.61-0.68 µm |
| NIR | 0.78-0.89 µm |
| SWIR | 1.58-1.75 µm |
Key characteristics of the Landsat TM and SPOT HRV sensors are compared in this summary table:
| Landsat TM | SPOT HRV | |
| Launch | 1982 | 1986 |
| Altitude | 705 km | 832 km |
| Attitude (polar) | 8.2° | 8.7° |
| Equatorial time | 09.45 | 10.30 |
| Swath width | 185 km | 60 km |
| Repeat coverage | 16 days | 26 days |
| Sensor | Thematic Mapper (TM) | High Resolution Visible (HRV) |
| Number of detectors | 100 | 6000/3000 |
| Advantages | Bands, swath size | Higher resolution, visual appearance of imagery |
| Bands | 7 | 1 + 3 |
| Scanner type | Mirror (7 cycles/second) | Pushbroom |
SPOT 6 and 7 imagery are provided by Satellite Imaging Corporation
http://www.satimagingcorp.com/satellite-sensors/.
Both SPOT 6 and 7 have a higher spatial resolution (1.5 meters -panchromatic and 6 meters -multispectral )compared to previous SPOT sensors. More information on SPOT 6 and 7 can be found in the above website.
Activity
Use these or other resources to further explore the characteristics of the SPOT system and particularly the characteristics of SPOT imagery that derive from the nature of the scanner technology and setup. Drawing also on relevant Landsat links provided in other learning objects, attempt to create an equivalent comparison table to that presented above for the very latest Landsat and SPOT scanners and post your table to the discussion forum.
The home page of the SPOT Program can be found at https://spot.cnes.fr/en/home-13 and the site contains an extensive gallery of SPOT images and application examples.