International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control
Li J., White P., Roche B., Bull J., Leighton T., Davis J.
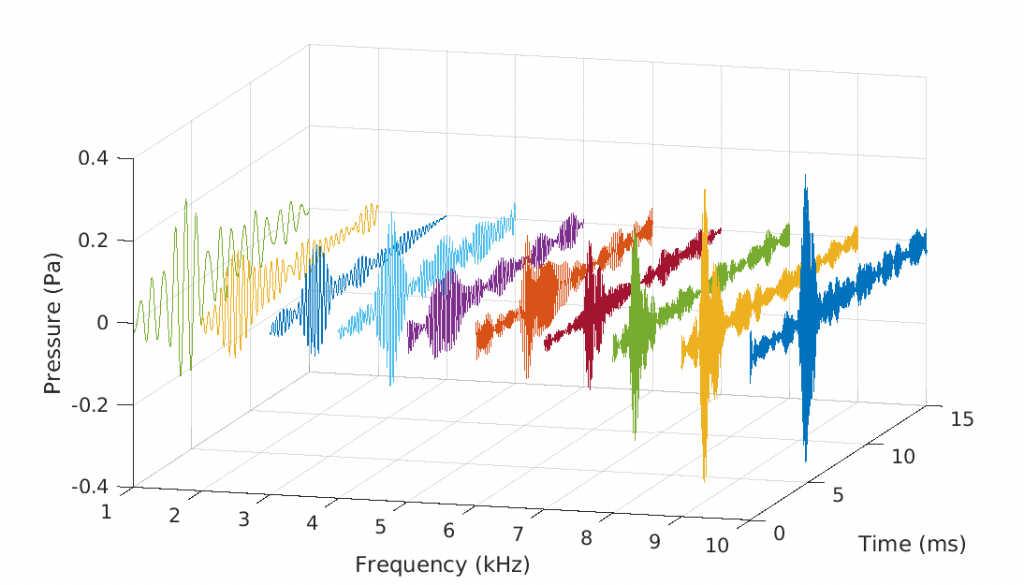
Passive acoustic techniques can be used to quantify underwater gas release. In this work we propose an adaptive single bubble identification technique, which incorporates bubble acoustic characteristics including pulsation time interval, frequency bandwidth and radiation strength. We demonstrate this technique using an array of hydrophones at a controlled CO2 release site, at 120m water depth in the central North Sea. The results show that the bubble radius, as estimated using acoustics has a distribution with a peak in the 0.15–0.3cm range, while an estimate based on optical method suggests a range of 0.2–0.5cm. The gas flux is acoustically estimated as 32–88kg/day in response to a known gas injection flow rate 143kg/day.