Looking back on the topics this module has covered so far this year, joint replacements and its future prospects particularly resonated with me. This is because a few of my family members have had knee replacements and for the most part it has completely changed their lives for the better. However, this is not always the case for people receiving joint replacements, and I believe further research into joint replacements is vital. So in this blog, I am going to explore the current problem with prosthetic joints and the exciting future prospects that have the potential to and are currently revolutionising joint replacements.
The Current Problem
The most common cause of replacement failure and revision of surgery is aseptic loosening, which is the loosening of the prosthesis from bone in the absence of infection or trauma. The main causes of aseptic loosening include Mechanical wear, particle debris, poor initial fixation and bone resorption and with the number of joint replacements surgeries increasing, it is paramount that we continue the research into the causes of aseptic loosening as this can reduce the revision burden. you can read more about the causes of aseptic loosening here: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877132720300385
Robotic-Assisted Joint Replacement
One of the most crucial developments in joint replacement is robotic-assisted surgery. Specialised sensors and software utilised by robots allow for more precise operations. This is because before surgery, it is used to produce a 3D image of the patients joint, therefore giving the surgeon the ability to create a customised surgical plan and the ideal implant sizes for that patient. Furthermore, it greatly reduces the risk of poor initial fixation (one of the causes for aseptic loosening) as the joint prosthetic is better aligned and stable due to the customised surgical plan. You can watch this video, which answers some of the questions around robotic-assisted surgery and how it compares to traditional surgery:
3D Printing: The Era of Custom Implants
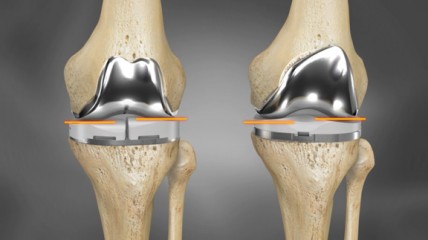
Another revolutionary advancement in joint prosthetics is 3D printing, which is enabling the production of fully customisable prosthetics and the creation of complex surgical models. It further enhances surgical precision, improving patient outcomes and expanding our understanding of what is surgically possible. Some of the benefits already being seen from 3D printing are enhanced fit and comfort, improved biocompatibility and integration, reduced surgery time and minimised complications. Overall, I believe that the 3D printing of prosthetics offers an exciting improvement to patient well-being following joint surgery, but it does raise the interesting question of will the future bring about implants constructed from bioengineered materials that integrate with our body flawlessly? Only time will tell, but current developments of scaffolds and hydrogels show promise. You can read more about 3D printing in surgery here: https://highsurgery.com/3d-printing-in-surgery-customizing-implants-and-surgical-models/
A Future Worth Anticipating
To me, it is clear that joint replacements are beginning to shift from a standardised mechanical solution to a more precise, personalised and effective approach. However, the development of joint prosthetics is far from over, and I believe that it is essential to utilise the continuing technological advancements to better joint replacements to further improve patient well-being post op.
References:
admin (2025). 3D Printing in Surgery: Customizing Implants and Surgical Models – HighSurgery. [online] HighSurgery. Available at: https://highsurgery.com/3d-printing-in-surgery-customizing-implants-and-surgical-models/.
Jones, M.D. and Buckle, C.L. (2020). How does aseptic loosening occur and how can we prevent it? Orthopaedics and Trauma, 34(3). doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mporth.2020.03.008.
Mills, J. (2024). The Evolution of Joint Replacement Surgery: How Technology is Changing Recovery Times. [online] Intelligent Living. Available at: https://www.intelligentliving.co/joint-replacement-surgery-techn-recovery/ [Accessed 28 Mar. 2025].
Ning, L., Gil, C., Hwang, B., Theus, A.S., Perez, L., Tomov, M.L., Bauser-Heaton, H. and Vahid Serpooshan (2020). Biomechanical factors in three-dimensional tissue bioprinting. 7(4), pp.041319–041319. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0023206.
www.orthoinfo.org. (n.d.). Robotic-Assisted Joint Replacement – OrthoInfo – AAOS. [online] Available at: https://www.orthoinfo.org/en/treatment/robotic-assisted-joint-replacement/.
This is a good blog. It nicely demonstrates a good understanding of organ-on-a-chip technology and clearly explains its purpose and…
This is a good blog, very engaging with a good backgroud to 3D bioprinting. You could improve your blog with…
This is a good, very interesting blog about necrobotics. It explores the idea of necrobiotics which is fairly new approach…
This is a good blog. You introduce the reader to the topic of prosthetics and bionic limbs in a very…
This is a good blog introducing hernia mesh benefits and drawbacks. You create a narrative in this blog, which showcase…