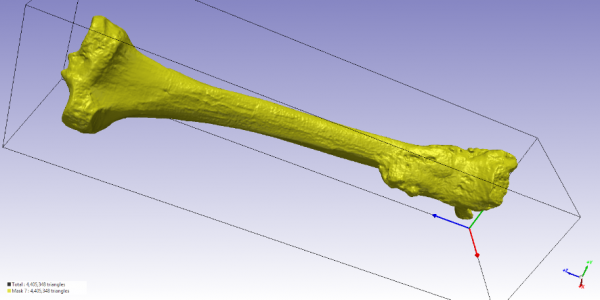
All the bones shown in “Stories” have been scanned using a technique called high resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT), which allows to visualise the inside of an object by transmitting an X-ray field through it. In this way, CT-scanners are able to record the internal and external details of a bone without damaging it.
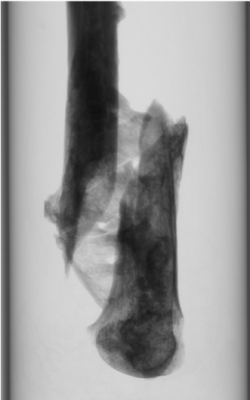
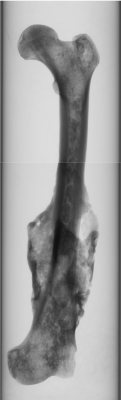
Using x-rays, the scanner produces a series of 2D images (cross-sectional views of the bone), which are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional model, like the one shown below. Such 3-D model is then converted into a mesh in order to perform a computational analysis of the bone.